FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
FIND ANSWERS TO COMMON QUESTIONS
Common questions about the Industrial Engineering ( IE ).
1. Who should study Industrial Engineering (IE)?
2. I have never heard of IE, is it a new area?
3. What is the different between other engineering disciplines and IE?
4. How is IE similar to other engineering disciplines?
5. What makes IE special from the other engineering disciplines?
6. What are the basic sciences for IE?
7. How do IE benefit society and business?
8. What classes will I take as an IE student?
9. What is the delivery mode in this programme?
10. Are IE only concerned with manufacturing?
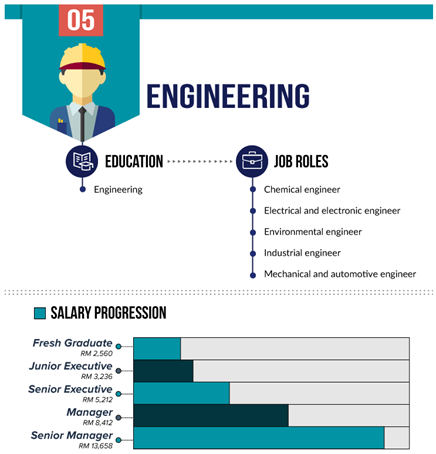
11. Where do the IE graduates work once they graduate?
12. What is the job scope for an Industrial Engineer?
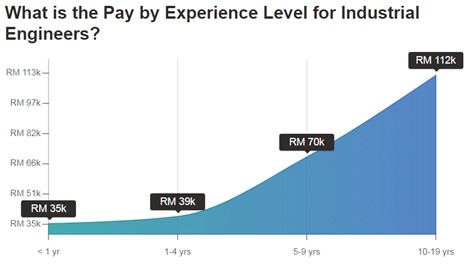
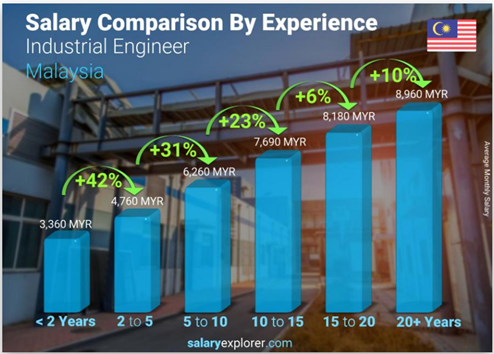
13. How much can Industrial Engineers earn?
14. Is the UTAR’s IE programme recognized by any government agency and/or professional body?
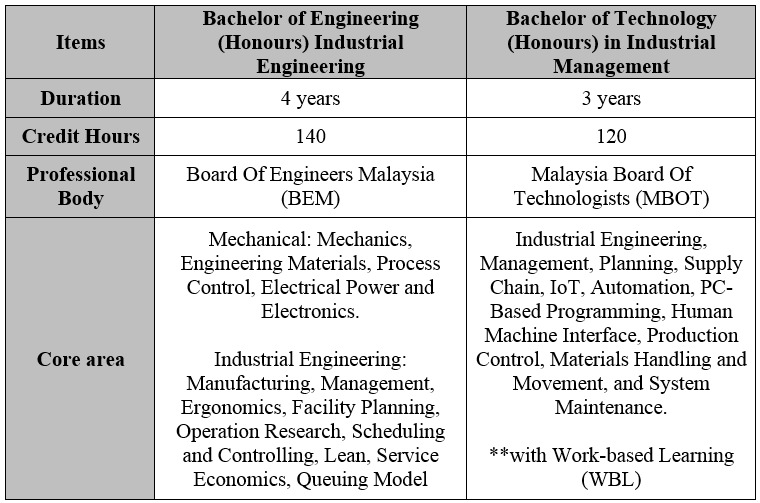
15. What is the main different between the Bachelor of Engineering (Honours) Industrial Engineering and Bachelor of Technology (Honours) in Industrial Management programmes that offered by UTAR?
1. Who should study Industrial Engineering (IE)?
Do you like solving problems? Are you interested in how things work? Do you like working with people? Are you an organizer? Do you like working on a team? Does using computers to solve practical problems interest you? Would you like to study a blend of business, management, and technical subjects? Are you interested in the way individual parts of a system work together? Are you looking for a challenge? If you answered yes, then you are suitable to study IE.
2. I have never heard of IE, is it a new area?
Yes and No. At UTAR, the IE programme has started mid of 2010 and the Department of Industrial Engineering was founded in 2011(before, the UTAR’s IE programme was parked under the Department of Electronics Engineering). Even though IE is relatively new in comparison to other engineering discipline, it is built on a strong foundation of traditions and skills that have been studied for over a hundred years. IE can trace many of its roots back to Frederick Taylor’s work in developing his theory of scientific management. In the early 1900s, as the world, and in particular the United States, was moving from an agrarian economy to a production economy, Taylor's initial studies into the science of work were attempts at solving some of the same problems that faced by Industrial Engineers. Central to the discipline of IE are two themes: the interfaces among people and machines within systems and the analysis of systems leading to improved performance. These issues motivated Taylor and make the IE of today.
3. What is the different between other engineering disciplines and IE?
Other engineering disciplines apply skills to very specific areas: Electrical Engineers are concerned with electrical systems and designing circuits, Mechanical Engineers are concerned with mechanical systems and building devices, Chemical Engineers are concerned with chemical systems and explore chemical processes, and Civil Engineers are concerned with physical systems and build structures. So what IE build? The short answer is that IE is involved in design processes and systems, which ultimately builds systems and processes; it is a quality and productivity building block for other engineering systems. Using knowledge of engineering, mathematics, business administration, and management, IE focuses on the way products and services are made and performed, though a combination of technical abilities, people skills, and business savvy, analysis, design, build, and management systems. IE is also involved in integrating of people, information, materials, and equipment that produce innovative and efficient organizations. In addition to manufacturing, IE is able to be applied in every industry, including hospitals, communications, e-commerce, entertainment, government, finance, food, pharmaceuticals, semiconductors, sports, insurance, sales, accounting, banking, travel, and transportation.
4. How is IE similar to other engineering disciplines?
IE take the same foundation courses in mathematics, physics, humanities, and social sciences. IE also take some of the basic physical engineering sciences like thermodynamic, circuits, statics, and solids. Like other engineering disciplines, IE employ mathematical models as a central device for understanding a system.
5. What makes IE special from the other engineering disciplines?
What sets IE apart from other engineering disciplines is IE emphasize on both people and technology. IE is unique among engineering disciplines in that its focuses on how people interact with a system. This concern for the human element leads to system designs that enhance the quality of life for all people. As a result, many Industrial Engineers have the leadership qualities necessary to advance in management. Industrial Engineers are often promoted to managerial positions sooner because of their training in leadership and in analyzing systems to improve productivity, quality, and profits. In addition, only few universities/institutions offer this discipline in Malaysia. Therefore, if you study IE, you are unique upon graduates.
6. What are the basic sciences for IE?
The fundamental of IE is Scientific Factory Management, which analyses and models production systems and services as queues and entities awaiting intervention from processes to reach a completed product that can function as a consumer good. These queues and entities can be further subdivided into smaller models, which form the basis of the courses offered by the IE programme in UTAR. These small building blocks require feasible solutions before it is able to be applied in industries facing various constraints, typically in the form of economics, production planning, facilities design, materials handling, manufacturing processes limitations, and job dues. With the advancement of computerized tools, simulation and optimization software performs the analysis. A strong background knowledge in IE building blocks will enable wise and accurate decision making when employing simulation and optimization software.
7. How do IE benefit society and business?
IE provides a systematic approach to streamlining and improving productivity and efficiency. Benefits that can be linked to IE include:
• Leaner, more efficient, and more profitable business practices while increasing customer service and quality.
• Improved competitiveness, profitability, and reduces resource requirements.
• Setting labor or time standards.
• Increased ability to do more with less.
• Making work safer, faster, easier, and more rewarding.
• Providing a method by which businesses can analyze their processes try to make improvements to them and helps to reduce waste in society.
• Reduce cycle time and increase throughput thus helping more people get their product quicker.
• Assistance in guiding society and business to care more for their workforce.
• Making the world safer through better designed and easier-to-use products.
• Reducing costs associated with new technologies, thus allowing more of the population to better their lives by being able to afford technological advances.
• Efficient and economical use of resources in an organization.
8. What classes will I take as an IE student?
On average, it takes four years to earn a Bachelor’s degree in IE. Typically, the first two years are spent studying basic sciences, introductory engineering (mechanical, electronic and electrical), the humanities and social sciences. During the last two years, most courses will concentrate on IE. IE have broad training in many areas including people-oriented techniques, design-oriented techniques, IE principles, applied engineering, computer techniques, production/industrial planning, scheduling and controlling. In addition, the broad learning experience allows students the flexibility to continue toward a Master's degree in Industrial Engineering. Courses in the IE undergraduate curriculum cover the following main focus areas: Manufacturing, Management, Ergonomics, Facility Planning, Operation Research, Scheduling and Controlling, Lean, and Service Economics.
9. What is the delivery mode in this programme?
Blended with lectures (theories and knowledge delivery), and practical/laboratory works (skills training and application). Besides, an industrial training for one trimester is also allocated for all students to experience the real working life and environment.
10. Are IE only concerned with manufacturing?
No. While IE was originally focused on manufacturing, IE is now evolved in the design of systems and processes to produce and deliver goods and services in all types of organization. IE work to integrate systems involving people, materials, facilities, finances, equipment, energy, and information. The objective is to achieve the best possible results in terms of quality, productivity, and safety. The benefit to you is that there is a huge variety of jobs available for you once you graduate.
11. Where do the IE graduates work once they graduate?
With its diversity, IE graduates appeals to a wide cross section of employers and you will have the opportunity to work in a variety of businesses and organizations. Since IE is focusing on integrating people, machines, and information to effectively, efficiently, and safely produce goods and services, the employment possibilities are endless. Common jobs that IE graduates can have in an organization include:
• Industrial Engineer (the main job) • Process Engineer
• QA/QC Engineer • Manufacturing Engineer
• Project Engineer • Manufacturing Consultant
• Product Engineer • Consultant
• Maintenance Engineer • Technical Service Engineer
• Inventory Controller • Technical Sales Engineer
• Systems Consultant/Engineer
12. What is the job scope for an Industrial Engineer?
Industrial Engineers figure out how to do things better. They make significant contributions to employers by saving money while making the workplace better for fellow workers. One of the main focuses of an Industrial Engineer is to improve the working environments of people – change the workplace while improving the worker. Industrial Engineer measure employee aptitude and motivation to encourage communication, morale, and leadership. Normally, Industrial Engineer will study Japanese management techniques such as Kaizen, Just-in-time delivery, Taguchi methods and Kanban.
13. How much can Industrial Engineers earn?
IE is a profession that offers you great variety and tremendous earning
power. According to the EduAdvisor, Engineering is the top 5 highest fresh graduate salaries in Malaysia 2019 and Industrial Engineer is one of the job roles that in the list.

(Source: EduAdvisor. 2019. The Highest Fresh Graduate Salaries in Malaysia 2019. [Online]. [9 November 2020]. Available from: https://eduadvisor.my/articles/the-highest-fresh-graduate-salaries-in-malaysia-2019/)
By referring to PayScale, the average salary for Industrial Engineer in Malaysia is 39,353 MYR annually. An Industrial Engineer typically makes between 4k - 124k MYR.

(Source: Payscale. 2020. Average Industrial Engineer Salary in Malaysia. [Online]. [9 November 2020]. Available from: https://www.payscale.com/research/MY/Job=Industrial_Engineer/Salary)
However, the survey result from salaryexplorer.com, a person working as an Industrial Engineer in Malaysia typically earns around 5,980 MYR per month. Salaries range from 2,870 MYR (lowest) to 9,390 MYR (highest). The experience level is the most important factor in determining the salary. Naturally the more years of experience the higher the wage.

(Source: Salaryexplorer. 2020. Industrial Engineer Average Salary in Malaysia 2020. [Online]. [9 November 2020]. Available from:
http://www.salaryexplorer.com/salary-survey.php?loc=130&loctype=1&job=481&jobtype=3)
*Note: the presented data is for references only.
14. Is the UTAR’s IE programme recognized by any government agency and/or professional body?
Yes. Our programme is approved by Malaysian Qualifications Agency (MQA) and accredited by Board of Engineers Malaysia (BEM). The UTAR’s IE programme prepares graduates to pursue registration as a Professional Engineer.
15. What is the main different between the Bachelor of Engineering (Honours) Industrial Engineering and Bachelor of Technology (Honours) in Industrial Management programmes that offered by UTAR?

